Nurturing our trees and getting fruits, veggies, or flowers from them is a joyous thing. Who doesn’t love planting trees? But what happens when our trees are not okay? If the white fungus has invaded it, how do you treat white fungus on plants? So, you may take the cure.
Fungal infections in the plants can reduce plant growth, hamper fruits, and so on. Moreover, if you have fungus on one plant, it can spread everywhere in your garden. So, it is mandatory to treat fungus on the plants.
Don’t worry. You can prevent and treat your plants from fungus invasion. How? I have plenty of treatment techniques and hacks for you. So, stay tuned and read out how to fight the plant fungus!
Recognizing the Fungal Appearance
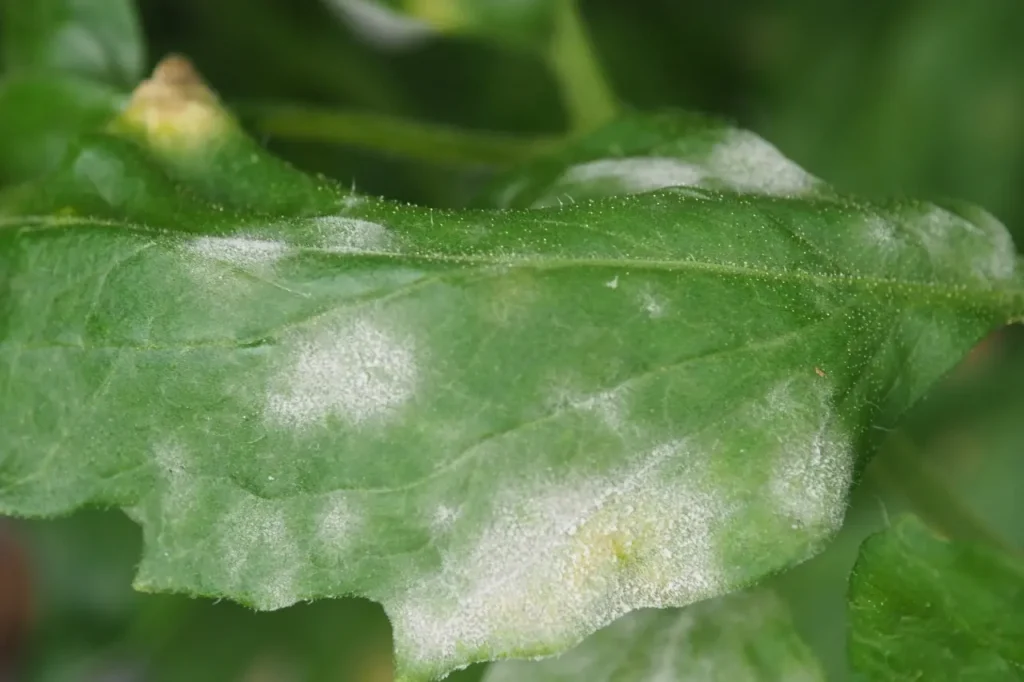
Once I was walking in my friend’s garden, and he told me about fungus on his plants. So, how does the white fungus on plants look? Initially, it is a white spot on the plant leaves and stems. Different types of fungus are there that cause fungal diseases. It has another name that is powdery mildew on plants. The fungal infection on plants varies in plant types, garden types, and seasons.
• White Fungus on plant leaves
Powdery mildew on the plant is a common thing that can happen in your garden. According to some findings belonging to the Michigan State University Extension, most plant diseases occur due to fungal pathogens, and the percentage is about 85%. Well, the number is massive. The white mold can attack your plant at any time. The powdery mildew is also dangerous as the black spot, rust, and blight. The types of fungus on the plant can be downy mildew, anthracnose, powdery mildew, and clubroot.
• White fungus on Stems and roots
Unlike the plant leaves, the stems and roots get the white fungus fuzz all over them. It is the fungus spores that spread so quickly on the infected plant. It looks like snow spread on your plant.
What is white fungus?
However, the fungus that causes the powdery mildew is Ascomycetes fungi. These fungi generally reproduce spores by asexual reproduction. “Sac fungi” is another name for Ascomycetes. It has conidio spores that generate the spores and spread uniformly over the plant. More specifically, the Uncinula necator, the scientific name of white ascomycetes fungi, is responsible for the powdery mildew. So, all of these are scientific staff that can help you know more about the white fungus and plans the proper treatment to save your plant in the future.
Factors that trigger the White fungus’s existence
Well, a lot of factors are responsible for white fungus disease. Initially, the environmental factors are temperature, pH, and airflow. The mid and late summer is the most appropriate time for powdery mildew. That means the June to September month.
However, environmental factors, along with the categories of plant species and gardening patterns, also trigger the white fungus on the plant. Let’s have a look at these by one:
• Environmental factors
More humidity and less airflow can trigger white mold formation. Initially, the white fungus is on the soil. It waits for the right time to attack the host, which means plants. Because in the late summer and spring, the spores try to reproduce by air, less airflow spreads the white mold effectively. The most favourable temperature is 15-32°C for the powdery mildew.
• Cropping pattern
Well, that is an acute one. If you plant your herbs, woody species, or other veggie species within a close distance, that will reduce the airflow of the garden or open plot. Eventually, the humidity will increase. Fertilizers are essential for plants, but excess nitrogen can initiate powdery mildew on your plant. On the other hand, one needs to water the plants carefully. Because wet leaves are more likely to cause white molds on the plant. So, overhead watering of the plants is best during brunch time when the weather is dry. Another note is not planting trees close to wet walls and fences that hinder the airflow.
• Types of plant species
There are different types of plant species that are prone to white fungus or white mold. The tomato, bean, squash, grapes, potato, and cabbage are one of those plants. Moreover, when there is Agro-forestry like a canopy, fruits, herbs, and shrubs all together, then pruning the shrubs is best to increase the airflow.
• White fungus on indoor or outdoor plant
White mold or powdery mildew on the plants can appear at any time. However, the white mold on the outdoor and greenhouse plant happens often.
Are white mold and powdery mildew of plants similar?
Many of you may get confused about what happened to your plant. The white mold and powdery mildew are identical a kind. White molds are fuzzy and create a cotton-like appearance, whereas the powdery mildew creates a white powder texture. Well, the powdery mildew on plants is an early stage of white mold. So, it is the sub-division of white mold. White mold is more likely to cause harm and health risks. So, powdery mildew is safe in terms of breakneck between these two.
Treatment approaches for the white fungus
Well, you can go for the quick remedies, chemical approach, biological approach, or somehow maintain your plot from such fungus. So let’s have a quick look at the treatment techniques for how do you treat white fungus on plants:
• Baking Soda: Okay, the quick and easy method to remediate the white fungus or powdery mildew is to use baking soda. A kitchen hack, I can say. Use one tablespoon of baking soda and half a tablespoon of liquid soap, mix with water, and spray your affected plant. You can pick other kitchen staff like compost tea aloevera extracts that strengthen your trees. And these are all 100 percent organic.
• Oil: Horticultural oil can be an option. You can use it if you see a little powdery mildew on your plants because some plants are sensitive to oil and hinder transpiration. You can also use sulfur to protect your plants from powdery mildew.
• Biological Fungicides: Like Pythium and Botrytis are biological fungicides. You can apply it to control the powdery mildew on plants.
• Gardening pattern: At first, you have to ensure the plant spacing. If you see powdery mildew on your plant leaves, cut them primarily, then treat the plant with a chemical or biological approach. Also, choosing citrus fruits, passion fruit, garlic, ginger, and onion as the companion plants can help to treat powdery mildew.
Application of fungicides
Treatment, at first sight, is the best option. Whenever the powdery mildew is on its way, try to apply organic remedies or fungicides to treat them. Best to use fungicides o 7-10 days intervals so that the plant can fight the fungus before harvest. Fungicides are not only for plant diseases, but you can apply them further for storage and grains.
At first, you will check the manufacturing specification, operating pressures, and nozzle sizes to spray your fungicides on the powdery mildew. And match the application of the fungicide with your plot criteria.
The best time to use your fungicide is related to the life cycle of the fungi responsible for powdery mildews. According to, Cornell University Long Island Horticultural Research and Extension Center Midday is the best time to put fungicides against the powdery mildew.
FAQ
So, let’s have some brainstorming sessions. Here are some questions that may arise in your mind while treating the white fungus on your plant. These faqs for you, if you are a beginner or sufferer due to white fungus on plants
How do you get rid of white powdery mold on plant?
Well, chemical and biological approaches can help you in this situation. You can apply fungicides to get rid of the fungus. Or you can adopt gardening techniques that keep your planting plot less humid to decrease the spore germination of the white fungus.
Is white mold on plants dangerous?
Undoubtedly. The white moulds are dangerous rather than powdery mildews on plants. Because moulds are all around the surroundings, only one factor is enough to trigger it. Whereas favourable seasons are essential for Powdery mildews.
Will powdery mildew go away?
It is a yes for this fungal plant disease. If the favourable season changes, the plant can recover from powdery mildew by itself. So, plant self-treatment can remove the fungus anyway.
Conclusion
Gardening is a laborious and fun task to do. Sometimes, commercial plant makers and gardeners find it difficult to cope with unwanted states of plants. White fungus on a plant is that kind. But treatment can help to reduce or remove it.
We all know that prevention is better than cure. So, before saying, ” why is there white fuzz on my plants?” We should do a little study about white fungus.
To sum up, integrated pest management, non-dense gardens, and a proper horticultural approach can lead to” no fungus” on people. So people, don’t be afraid of those white, powdery mildew on your plant. You can treat it anyway!

